Create a mesh
With Ultimaille, you can create many type of mesh. Surface mesh, like triangular (tri) mesh or quadrangular (quad) mesh and volume mesh like tetrahedral (tet) mesh or hexahedral (hex) mesh.
Surface mesh
Tri mesh
Tri mesh is a surface mesh where facets are triangles. All you have to do is create a Triangle and the mesh points, then facets and link each vertex facet to a point.
Note
As mesh is a tri mesh, each facet has exactly 3 points. A triangle that have 2 or more vertex on the same point is degenerate.
// Declare a mesh with triangle surface
Triangles m;
// --- CREATE ---
// Create 5 points in mesh
m.points.create_points(5);
m.points[0] = vec3(0.,0.,0.);
m.points[1] = vec3(1.,0.,0.);
m.points[2] = vec3(0.5,1.,0.);
m.points[3] = vec3(1.5,1.,0.);
m.points[4] = vec3(1.,2.,0.);
// Create 5 facets
m.create_facets(3);
// Link facet 0, vertex 0 with point 0
m.vert(0, 0) = 0;
// Link facet 0, vertex 1 with point 1
m.vert(0, 1) = 1;
// Link facet 0, vertex 2 with point 2
m.vert(0, 2) = 2;
// Link facet 1, vertex 0 with point 1
m.vert(1, 0) = 1;
// ...
m.vert(1, 1) = 3;
m.vert(1, 2) = 2;
m.vert(2, 0) = 2;
m.vert(2, 1) = 3;
m.vert(2, 2) = 4;
Save the mesh as seen previously:
// Save mesh
write_by_extension(output_dir + "tri_mesh.geogram", m);
With this code, you would have this simple surface mesh:
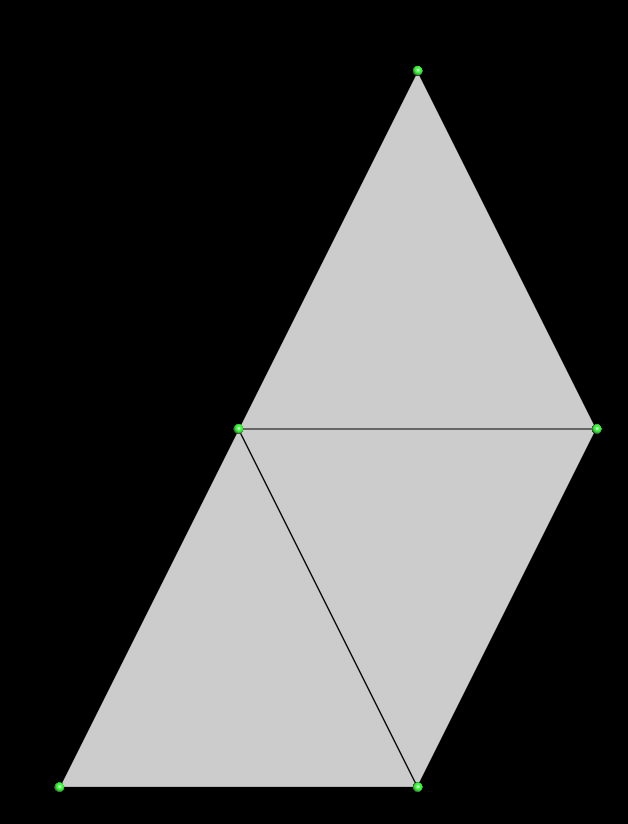
Quad mesh
Quad mesh is a surface mesh where facets are quadrangles. All you have to do is create a Quad and the mesh points, then facets and link each vertex facet to a point.
Note
As mesh is a quad mesh, each facet has exactly 4 points. A quadrangle that have 2 or more vertex on the same point is degenerate.
// Init a Quad mesh
// We will create a cube
Quads m;
// Create and place 8 points
m.points.create_points(8);
m.points[0] = vec3(-1, -1, 1);
m.points[1] = vec3(1, -1, 1);
m.points[2] = vec3(1, -1, -1);
m.points[3] = vec3(-1, -1, -1);
m.points[4] = vec3(-1, 1, 1);
m.points[5] = vec3(1, 1, 1);
m.points[6] = vec3(1, 1, -1);
m.points[7] = vec3(-1, 1, -1);
// Create cube facets
m.create_facets(6);
// Link facet 0, vertex 0 with point 0
m.vert(0, 0) = 0;
// Link facet 0, vertex 1 with point 1
m.vert(0, 1) = 1;
// ...
m.vert(0, 2) = 2;
m.vert(0, 3) = 3;
// Link facet 1, vertex 0 with point 4
m.vert(1, 0) = 4;
// ...
m.vert(1, 1) = 5;
m.vert(1, 2) = 6;
m.vert(1, 3) = 7;
m.vert(2, 0) = 0;
m.vert(2, 1) = 1;
m.vert(2, 2) = 5;
m.vert(2, 3) = 4;
m.vert(3, 0) = 3;
m.vert(3, 1) = 2;
m.vert(3, 2) = 6;
m.vert(3, 3) = 7;
m.vert(4, 0) = 0;
m.vert(4, 1) = 4;
m.vert(4, 2) = 7;
m.vert(4, 3) = 3;
m.vert(5, 0) = 1;
m.vert(5, 1) = 5;
m.vert(5, 2) = 6;
m.vert(5, 3) = 2;
// Connect mesh
m.connect();
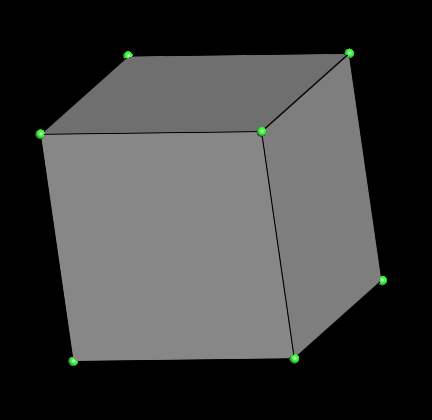
Volume mesh
Tet mesh
[Coming soon]
Hex mesh
Hex mesh is a volume mesh where cells are hexahedra. All you have to do is create a Hexahedra and the mesh points, then cells and link each vertex cells to a point.
// Declare a mesh with hex cells
Hexahedra m;
// --- CREATE ---
// Create and place 8 points
// /!\ There is a vertex numbering convention (https://github.com/ultimaille/ultimaille/tree/master/notes/mesh_vertex_numbering_convention.pdf),
// it gives a specific order of vertex to be able to rely them correctly
// Here, this order is given by following points declaration
// Therefore, we just have to associate vertex i with point i (m.vert(0,i) = i)
// Note that we could have declared them in any order, but if we did, we'd have to link them in the right order
m.points.create_points(8);
m.points[0] = vec3(-0.5,-0.5,-0.5);
m.points[1] = vec3(0.5,-0.5,-0.5);
m.points[2] = vec3(-0.5,0.5,-0.5);
m.points[3] = vec3(0.5,0.5,-0.5);
m.points[4] = vec3(-0.5,-0.5,0.5);
m.points[5] = vec3(0.5,-0.5,0.5);
m.points[6] = vec3(-0.5,0.5,0.5);
m.points[7] = vec3(0.5,0.5,0.5);
// Create 1 cell
m.create_cells(1);
// Link cell 0, vertex 0 with point 0
m.vert(0, 0) = 0;
// Link cell 0, vertex 1 with point 1
m.vert(0, 1) = 1;
// ...
m.vert(0, 2) = 2;
m.vert(0, 3) = 3;
m.vert(0, 4) = 4;
m.vert(0, 5) = 5;
m.vert(0, 6) = 6;
m.vert(0, 7) = 7;
// --- SAVE ---
// Save mesh
write_by_extension(output_dir + "hex_mesh.geogram", m);
Polyline
Polyline are just line segments linked together. You have to create a Polyline and it's points, then relies them.
// Declare a polyline
PolyLine p;
// --- CREATE ---
// Create 5 points in polyline
p.points.create_points(5);
p.points[0] = vec3(0, 0, 0);
p.points[1] = vec3(1, 0, 0);
p.points[2] = vec3(1, 1, 0);
p.points[3] = vec3(0, 1, 0);
p.points[4] = vec3(0.5, 0.5, 1);
// Create edges
p.create_edges(8);
// Link segment 0 with point 0
p.vert(0, 0) = 0;
// Link segment 0 with point 1
p.vert(0, 1) = 1;
// Link segment 1 with point 0
p.vert(1, 0) = 1;
// ...
p.vert(1, 1) = 2;
p.vert(2, 0) = 2;
p.vert(2, 1) = 3;
p.vert(3, 0) = 3;
p.vert(3, 1) = 0;
p.vert(4, 0) = 0;
p.vert(4, 1) = 4;
p.vert(5, 0) = 1;
p.vert(5, 1) = 4;
p.vert(6, 0) = 2;
p.vert(6, 1) = 4;
p.vert(7, 0) = 3;
p.vert(7, 1) = 4;
EdgeAttribute<int> edge_attr(p);
edge_attr[0] = 0;
edge_attr[1] = 1;
// --- SAVE ---
// Save mesh
write_by_extension(output_dir + "pyramid.geogram", p, {{"my_edge_attr", edge_attr}});