How to ?
This section gives a quick overview of how to use ultimaille for:
- Create a project from scratch
- Load / save a mesh
- Browse a mesh
- Create a mesh
- Edit a mesh
- Read / write attributes
- Work on geometry of primitives
- Visualize results
- Use algebra
Generalities
What is a mesh
Polygonal mesh
In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of vertices, edges and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object. The faces usually consist of triangles (triangle mesh), quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polygons (n-gons), since this simplifies rendering, but may also be more generally composed of concave polygons, or even polygons with holes. wiki
Volume mesh
In 3D computer graphics and modeling, volumetric meshes are a polygonal representation of the interior volume of an object. Unlike polygon meshes, which represent only the surface as polygons, volumetric meshes also discretize the interior structure of the object. wiki
Meshes in Ultimaille
Surface mesh
Ultimaille handles surface meshes such as triangular meshes - whose faces are triangles, quadrangular meshes - whose faces are quadrilaterals - and, more generally, polygonal meshes. For each type of surface, ultimaille has the corresponding classes: Triangles, Quads, Polygons.
Ultimaille provides interfaces for accessing the different primitives of these meshes: vertices, faces, edges or, more precisely, half-edges and corners.
Volume mesh
Ultimaille also handles volume meshes: tetrahedral, hexahedral, pyramidal, wedges corresponding respectively to the classes: Tetrahedra, Hexahedra, Pyramids, Wedges.
Primitives
A mesh is composed of elements named primitives, different type of primitives are:
- Vertex: a 3D position
- Half-edge: an oriented edge into the face that relies two vertices
- Face: a set of half-edges
- Cell (in volumetric meshes only): a set of faces
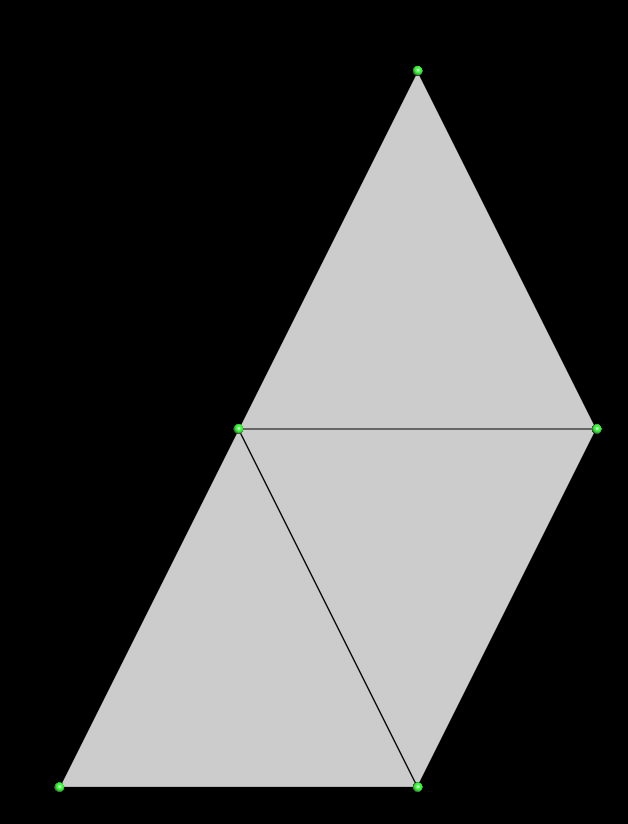
Vertex
A vertex is a 3D point in space, which are generally connected by the edges of a face. Below, you can see vertices of 3 triangles in green.
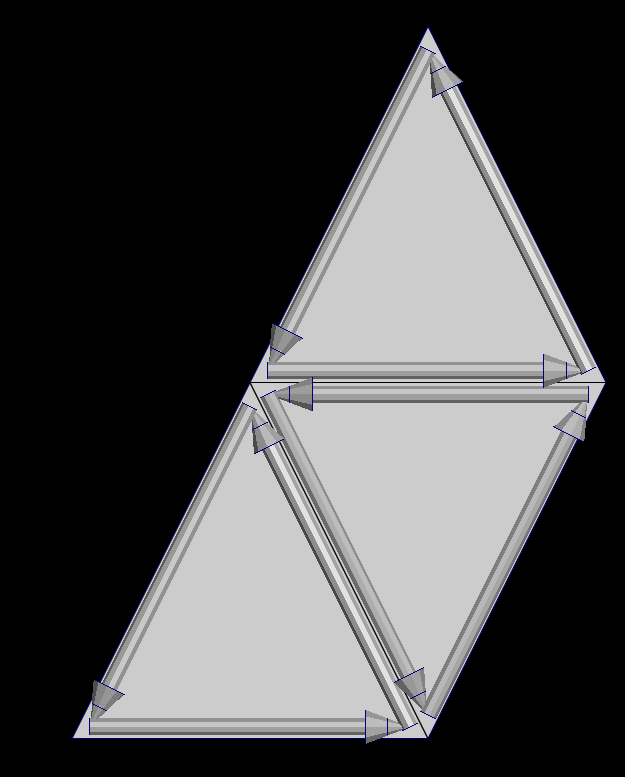
Half-edge
A half-edge is a data structure that represents oriented edges which are contained by the faces and follow its contour. Each face have a set of half-edges and more important, each half-edge knows his previous, next and opposite half-edge. We'll see later how useful this is when we want to traverse a mesh.
Note
You can find all the examples in this tutorial in the following repository: ultimaille-examples